Wirkungsgrad η
Der elektrische Wirkungsgrad η ist das Verhältnis aus dem nutzbaren Anteil einer elektrischen Größe zur zugeführten Menge dieser elektrischen Größe.
Wirkungsgrad:
Leistungsanpassung: Ri = Ra [Zi = Za]
ηP =
η = Wirkungsgrad [1]
P = Leistung (Last) [W]
P0 = Bezugsleistung (Quelle) [W]
Ra = Lastwiderstand [Ω]
Ri = Quellwiderstand [Ω]
Stromanpassung: Ri ≫ Ra [Zi ≫ Za]
ηI =
η = Wirkungsgrad [1]
I = Strom [A]
UL = Leerlaufspannung [V]
Ra = Lastwiderstand [Ω]
Ri = Quellwiderstand [Ω]
Spannungsanpassung: Ri ≪ Ra [Zi ≪ Za]
ηU =
ηU = Wirkungsgrad (Spannungsanpassung) [1]
I = Strom [A]
U = Spannung [V]
Ra = Lastwiderstand [Ω]
Ri = Quellwiderstand [Ω]
Antennenwirkungsgrad η:
ηAntenne =
η = Antennenwirkungsgrad [1]
P = Leistung (abgestrahlte Leistung) [W]
P0 = Bezugsleistung [W]
PS = Strahlungsleistung [W]
PE = Eingangsleistung [W]
G = Antennengewinnfaktor [1]
D = Richtfaktor [1]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [Ω]
RV = Verlustwiderstand [Ω]
Wirkungsgrad η bei Anpassung:
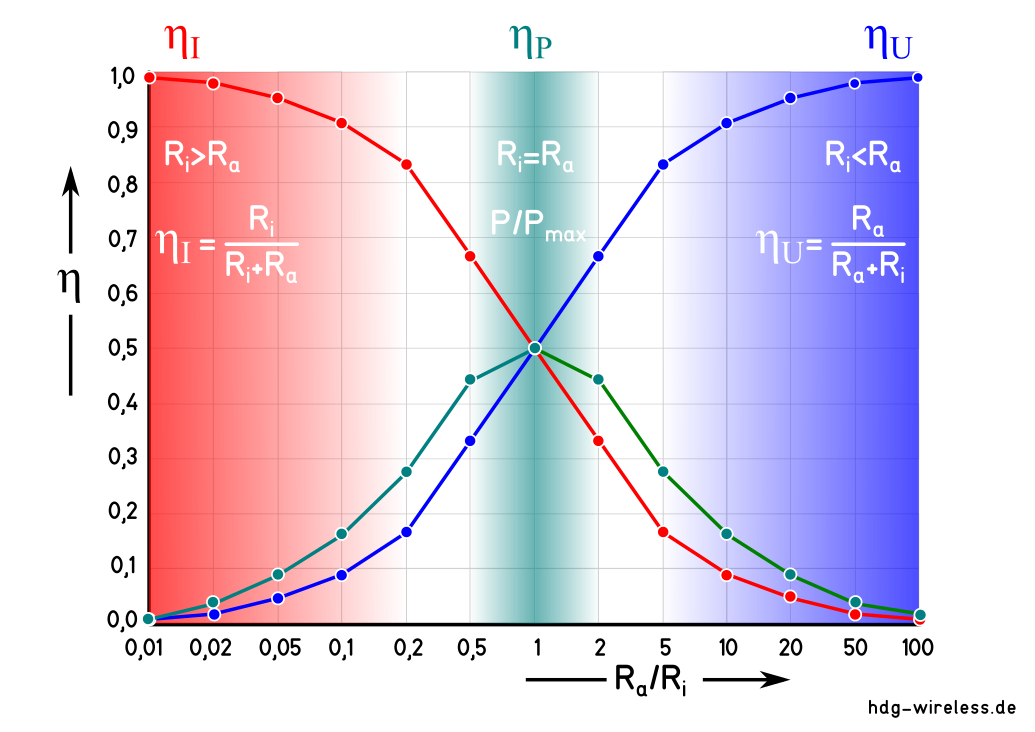
η = Wirkungsgrad [1]
I = Strom [A]
P = Leistung [W]
U = Spannung [V]
Ri = Quellwiderstand [Ω]
Ra = Lastwiderstand [Ω]
Der Wirkungsgrad η einer Anpassungsschaltung bei Stromanpassung (Ri ≫ Ra), Spannungsanpassung (Ri ≪ Ra) und Leistungsanpassung Ri = Ra berechnet sich aus dem Verhältnis vom Quellwiderstand Ri zum Lastwiderstand Ra.
Der Wirkungsgrad η kann dabei Werte zwischen 0 und 1 annehmen.
Der Wirkungsgrad η bei Leistungsanpassung Ri = Ra beträgt 50 %.
Die Hälfte der verfügbaren Leistung P ist die maximale Leistung Pmax, die der Außenwiderstand Ra aufnehmen kann.
Die andere Hälfte geht als Verlustleistung PV im Innenwiderstand Ri der Quelle verloren.
